HomFax Forensic Hub
Developer Specification & Visual Architecture
The complete developer-grade blueprint for the Ambassador platform's forensic single-source-of-truth. Tamper-evident property history, cryptographic proofs, AI-powered damage analysis, and smart-contract integration.
Introduction
High-Level Summary
HomFax is the Ambassador platform's forensic single-source-of-truth. It is a tamper-evident property-history and forensic-documentation subsystem that ingests and corroborates multi-source evidence, records cryptographic hashes on a distributed ledger, and issues verifiable HomFax reports that trigger smart-contract actions. Built for audit, dispute resolution, and automated settlement, HomFax converts photos, sensor feeds, municipal records, and expert entries into hash-verified evidence and fraud alerts, ensuring every milestone payment and warranty claim is driven by provable, immutable proof.
Core Responsibilities
Ingest and normalize evidence from various sources, including binary files and structured metadata.
Compute cryptographic hashes and batch proof structures, anchoring proofs to a distributed ledger.
Run AI-powered forensic analysis to classify damage, determine severity, and differentiate pre-existing from new damage.
Store large files off-chain with immutable references (S3/IPFS) and provide fast CDN access.
Produce Verifiable HomFax Reports and Fraud Alerts for portals, insurers, and smart contracts.
Provide secure APIs, event webhooks, and an admin UI for QA, forensic review, and integration.
System Architecture
VerifiedThe overall system architecture is designed for scalability, security, and verifiability. It separates concerns into distinct layers, from evidence input to on-chain anchoring and final consumption by various stakeholders.

Architectural Components
| Layer | Component | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Inputs | Evidence Sources | Inspector uploads, IoT/weather feeds, municipal records, and manual expert entries. |
| Ingestion | Data Ingestion Layer | Secure API endpoints (REST/GraphQL) with JWT/mTLS auth and Kafka/RabbitMQ queuing. |
| Storage | Off-Chain Storage | Encrypted, versioned object storage (AWS S3/IPFS) with CloudFront CDN. |
| AI Pipeline | Forensic AI Pipeline | Multi-stage pipeline: preprocessing, feature extraction, damage classification, severity scoring. |
| Hashing | Hashing & Proof Engine | SHA-256 hashing, Merkle trees for batching, and ECDSA digital signatures. |
| Ledger | HomFax Ledger | Append-only MongoDB database for property history, evidence records, and audit trails. |
| Blockchain | Blockchain Anchor | Smart contract bridge anchoring Merkle roots to Polygon for public verifiability. |
| Outputs | HomFax Outputs | Verifiable reports, fraud alerts, smart contract triggers, and audit trail records. |
| Consumers | Consumer Portals | Role-based web portals for Homeowners, Contractors, Insurers, Attorneys, Inspectors. |
| Execution | Smart Contract Engine | Deploys contracts, releases milestone payments, manages dispute resolution. |
Evidence Lifecycle & Data Flow
VerifiedThe lifecycle of a piece of evidence is a critical workflow that ensures integrity and verifiability at every step. The process is designed to be automated, secure, and auditable.

Lifecycle Stages
Upload & Ingest
Evidence is submitted via a secure API, authenticated, and streamed to S3, while metadata is extracted.
Hash & Sign
A SHA-256 hash is computed for the file. A canonical JSON record is created, hashed (record_hash), and signed by the inspector.
AI Forensic Analysis
The evidence undergoes a detailed AI pipeline analysis, with the results appended to the record.
Fraud Detection
The record is checked against a rules engine and ML models. Anomalies trigger alerts and may pause the workflow.
On-Chain Anchoring
The record_hash is batched into a Merkle tree, and the merkle_root is anchored to the Polygon blockchain.
Report Generation
A verifiable HomFax Report is generated, hashed, and stored. A webhook notifies subscribed systems.
Smart Contract Actions
The Smart Contract Execution Engine receives the verified event and triggers the appropriate on-chain action.
Upload → Hash → Anchor (Pseudocode)
# 1. Upload files to S3 (presigned)
upload_files_to_s3(files)
# 2. For each file compute SHA-256
for f in files:
f.file_hash = sha256(f.stream)
# 3. Build evidence JSON (canonical)
record = canonicalize({
property_id: pid,
claim_id: cid,
files: files_meta,
metadata: meta
})
record_hash = sha256(json_canonical(record))
# 4. Store 'pending' record in DB
db.insert('evidence_records', {
..., record_hash: record_hash,
status: 'pending'
})
# 5. Queue AI job
# After AI completes: update record.ai_analysis
# 6. When ready to anchor:
# Build Merkle root, call anchor contract
tx = homfax_anchor_contract.anchor(
propertyId, claimId,
merkleRoot, metadataCid
)
await tx.wait()
# 7. Update DB with onchain_anchor
# { tx_hash, block }Data Model & Schemas
VerifiedThe data is modeled using a document-oriented approach (MongoDB) to accommodate the flexible, nested structure of forensic records. Key collections are indexed for performance on common query patterns such as property_id, timestamps, claim_id, and verification_status.

properties Collection
{
"_id": "property_0001",
"address": {
"street": "312 English Oak St",
"city": "Georgetown",
"state": "TX",
"zip": "78626"
},
"parcel_id": "R012345",
"owner": {
"name": "Jane Doe",
"contact": "[email protected]",
"user_id": "usr_001"
},
"homfax_summary": {
"last_report_id": "report_123",
"fraud_score": 0.02
},
"created_at": "2026-02-07T12:00:00Z",
"updated_at": "2026-02-07T12:00:00Z"
}evidence_records Collection
{
"_id": "evid_0001",
"property_id": "property_0001",
"claim_id": "claim_123",
"uploader": {
"id": "user_45",
"role": "inspector",
"signature_pubkey": "0x04a1b2c3..."
},
"source": "inspection",
"files": [{
"filename": "roof_damage_01.jpg",
"content_type": "image/jpeg",
"size": 345678,
"storage_uri": "s3://homfax/props/xxx/img1.jpg",
"file_hash": "sha256:a1b2c3d4e5f6..."
}],
"ai_analysis": {
"damage_type": "wind",
"severity": "moderate",
"confidence": 0.93,
"preexisting": false,
"explanations": {
"bbox": [120, 80, 340, 260],
"saliency_map_uri": "s3://homfax/..."
}
},
"metadata_hash": "sha256:meta1234...",
"record_hash": "sha256:record5678...",
"onchain_anchor": {
"tx_hash": "0xabc123...",
"chain": "polygon",
"block": 123456
},
"verification": {
"verified": true,
"verified_at": "2026-02-07T13:00:00Z",
"verified_by": "system"
},
"status": "verified",
"audit": [{
"event": "upload",
"by": "user_45",
"at": "2026-02-07T12:30:00Z"
}]
}homfax_reports Collection
{
"_id": "report_123",
"property_id": "property_0001",
"claim_id": "claim_123",
"compiled_records": [
"evid_0001",
"evid_0002"
],
"report_hash": "sha256:repab12...",
"report_uri": "s3://homfax/reports/report_123.pdf",
"fraud_alerts": [],
"signatures": [{
"role": "inspector",
"signature": "0x3045...",
"pubkey": "0x04a1b2c3..."
}],
"created_at": "2026-02-07T14:00:00Z"
}Cryptographic Anchoring & Verification
Verified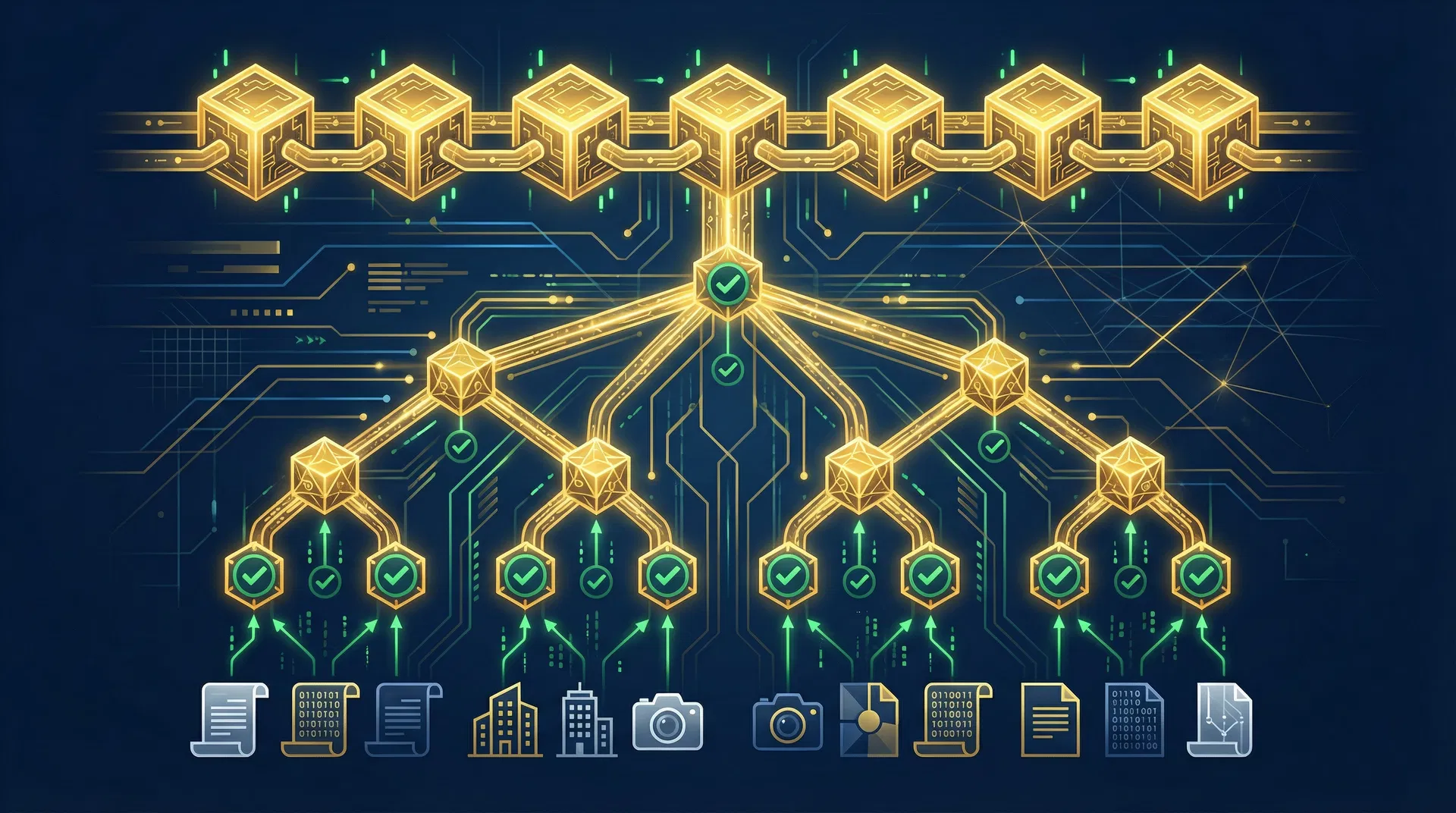
Merkle tree batching and blockchain anchoring for tamper-evident proof
The cryptographic engine is the core of HomFax's tamper-evident guarantee. It combines hashing, digital signatures, and blockchain anchoring to create a verifiable chain of custody.

Key Cryptographic Primitives
Anchor Contract Call
const tx = await homfaxAnchorContract.anchor(
propertyId,
claimId,
merkleRoot,
metadataCID,
{ gasLimit: 200000 }
);
const receipt = await tx.wait();
console.log("Anchored at block:", receipt.blockNumber);
console.log("TX hash:", receipt.transactionHash);Verify Proof (Consumer)
// Given a report with record_hash,
// merkleProof, and anchorRoot:
const isMember = merkle.verify(
merkleProof,
recordHash,
root
);
const onchainRoot = getRootFromChain(txHash);
return isMember && (onchainRoot === root);
// => true = tamper-proof verifiedForensic AI Pipeline
Verified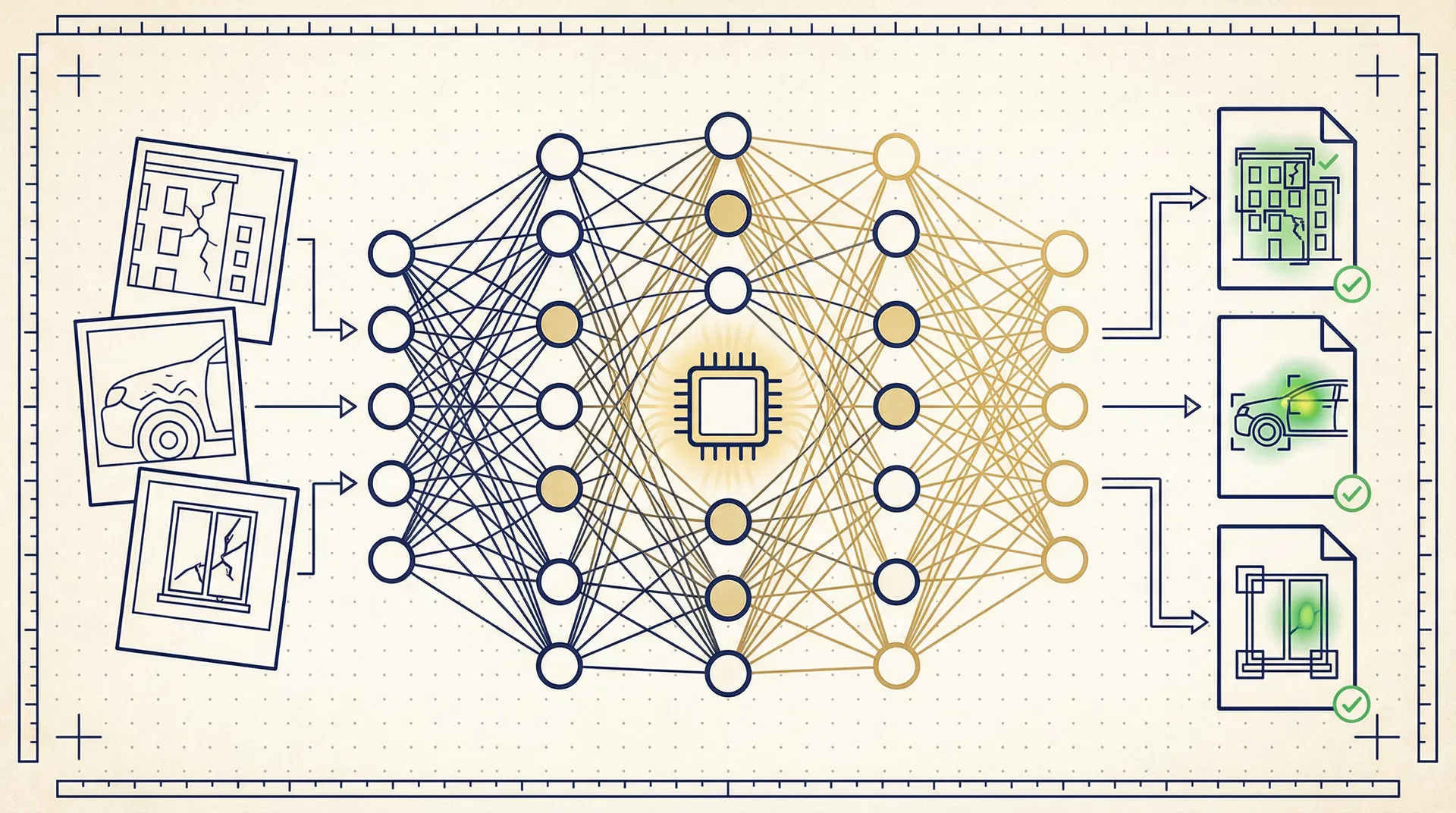
The AI pipeline automates the analysis of visual evidence, providing objective, consistent, and scalable damage assessments. It processes images through multiple specialized neural network heads for comprehensive forensic analysis.

Pipeline Stages
1. Preprocessing
Normalizes images, corrects orientation via EXIF, and merges multi-modal data (thermal + visible light). Temporal pairing for before/after comparison.
2. Feature Extraction
A CNN backbone (ResNet, ConvNeXt, or EfficientNet) extracts high-dimensional feature embeddings from preprocessed images.
3. Task Heads
Multiple specialized heads: Damage Classification (multi-label: wind, hail, water, fire, impact), Severity Regression (0.0–1.0), Pre-existing Classifier, and Instance Segmentation (Mask R-CNN / SAM).
4. Ensemble & Calibration
Combines vision outputs with metadata (timestamp, weather event proximity, GPS) and applies temperature scaling for calibrated confidence scores.
5. Explainability
Generates Grad-CAM saliency heatmaps, bounding box annotations, and natural language explanations for each decision. Artifacts stored to off-chain storage.
API Specification
The HomFax hub exposes a set of secure REST/GraphQL endpoints for interaction. All endpoints require authentication (JWT) and may require mTLS for corporate partners.
Endpoints
| Method | Endpoint | Auth | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| POST | /v1/homfax/inspections | JWT + mTLS | Upload an inspection package (files + metadata). Triggers the entire evidence lifecycle. |
| GET | /v1/homfax/records/{id} | JWT | Fetch the full JSON for a specific evidence record. |
| POST | /v1/homfax/verify | JWT (Inspector/Insurer) | Request verification or re-verification of a record or report. |
| GET | /v1/homfax/reports/{id} | JWT | Download a verifiable HomFax Report (signed JSON + PDF URI + anchors). |
| GET | /v1/homfax/property/{id}/history | JWT | Retrieve the paginated forensic history for a given property. |
| POST | /v1/homfax/webhook/register | JWT (Admin) | Register a webhook to subscribe to HomFax events. |
Webhook Events
HomFaxReportGeneratedA new verifiable report has been compiled and anchored.
FraudAlertRaisedAn anomaly was detected during evidence analysis.
OnchainAnchorCommittedA Merkle root has been successfully anchored on-chain.
VerificationFailedA record or report failed integrity verification.
RecordUploadedNew evidence has been uploaded and is pending processing.
AIAnalysisCompleteAI forensic analysis has finished for a record.
Webhook Payload Example
{
"event": "HomFaxReportGenerated",
"report_id": "report_123",
"property_id": "property_0001",
"claim_id": "claim_123",
"report_hash": "sha256:repab12...",
"onchain_anchor": {
"tx_hash": "0xabc123...",
"block": 12345
}
}Security & Access Control
VerifiedSecurity is paramount. The system employs a multi-layered security model to protect data integrity, confidentiality, and availability. All communications must use HTTPS/TLS 1.3, and all data at rest is encrypted with AES-256.

Security Layers
Authentication
OAuth2/JWT for users, mTLS for system-to-system communication.
Authorization
Strict RBAC: Admin, Inspector, Contractor, Insurer, Auditor, System.
Encryption
AES-256 at rest (SSE-KMS), TLS 1.3 in transit, certificate management.
Key Management
AWS KMS or HashiCorp Vault with strict access policies and rotation.
Tamper Protection
Append-only writes, cryptographic hashing, digital signatures, blockchain anchors.
Auditing
Structured JSON logs, distributed tracing (OpenTelemetry), comprehensive access logging.
RBAC Role Matrix
| Role | Permissions |
|---|---|
| Admin | Full system access, key rotation, user management |
| Inspector | Upload, sign, verify own records |
| Contractor | View assigned claims, submit milestones |
| Insurer | Read reports, verify, dispute management |
| Auditor | Read-only audit trail, chain-of-custody |
| System | Automated services: anchor, AI, report generation |
Deployment & Infrastructure
The platform is designed for a cloud-native deployment on AWS, leveraging a containerized architecture managed by Kubernetes (EKS) for scalability and resilience.

Recommended Technology Stack
| Category | Technology |
|---|---|
| Cloud Provider | AWS (S3, EKS, CloudFront, KMS) |
| Container Orchestration | Amazon EKS (Kubernetes) |
| Message Queue | Apache Kafka or RabbitMQ |
| Database | MongoDB Atlas (Replica Set) |
| Object Storage | AWS S3 with Object Lock (WORM) |
| CDN | AWS CloudFront |
| Security | AWS WAF, KMS, HashiCorp Vault |
| Blockchain | Polygon (Mainnet + Mumbai testnet) |
| Observability | OpenTelemetry, CloudWatch, Grafana |
| AI Inference | GPU nodes (gRPC/REST endpoints) |
90-Day Development Roadmap
The following Gantt chart outlines a proposed 90-day development plan to deliver the Minimum Viable Product (MVP) of the HomFax Forensic Hub.

Phase Summary
Foundation
Core Ingestion API, S3 storage, canonicalizer, DB, and basic record hashing.
Crypto Engine
Hashing engine, Merkle root batcher, anchor service (Hardhat), ECDSA module.
AI Pipeline
Image preprocessing, CNN model training, severity scoring, pre-existing detection, GPU inference.
Reports & Fraud
Verifiable report generator, webhook system, fraud rules engine, ML anomaly model.
Integration
Smart contract bridge (testnet), admin UI/QA dashboard, end-to-end tests.
Hardening
Security pen testing, scalability testing, compliance review, production rollout.
References & Resources
Ambassador Patent
"A System and Method for Blockchain-Based Property Claim Lifecycle Management..." (U.S. Non-provisional Patent Application, Patent Pending: US 63/741,861)
Ambassador Smart Contract System Agreement
Defines the HomFax Ledger, Verifiable HomFax Reports, and the claim workflow.
Ambassador QualityChain Deployment Guides
Provides scripts and configurations for smart contract deployment and anchor patterns.
Related Links
Contact: [email protected] | (800) 701-7663
Owner: Regulus Development Corporation (RDC LLC) | Version 1.0 | February 2026